Pharmaceutical Aggregation: Securing the Supply Chain
What is Pharmaceutical Aggregation?
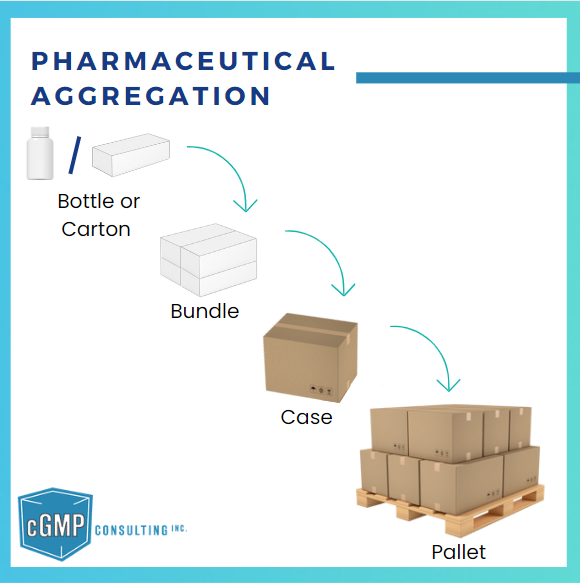
Pharmaceutical aggregation is the process of creating a hierarchical relationship between different levels of serialized packaging, such as cartons, cases, and pallets. This hierarchy allows each packaging level to be uniquely identified and linked in a “parent-child” structure, enabling accurate tracking and traceability of pharmaceutical products throughout the supply chain.
How Does Aggregation Work?
In the aggregation process, each packaging level receives a unique identifier. For example:
- Carton (Child): Each carton containing individual units is serialized with a unique identifier.
- Case (Parent): The case that holds multiple cartons is also assigned a unique identifier, which links back to each carton inside.
- Pallet (Parent): A pallet containing several cases is assigned another identifier, linking it to the individual cases.
These “parent-child” relationships ensure that each packaging level is linked to the next, forming a traceable hierarchy.
Importance of Aggregation in the Pharmaceutical Industry
- Enhancing Supply Chain Traceability
Aggregation plays a critical role in ensuring that products can be tracked at every stage of their journey, from manufacturing to distribution, and ultimately to the customer. This enables manufacturers and regulatory bodies to trace the exact origin of a product, detect any irregularities, and ensure its authenticity. - Improving Product Safety and Security
By establishing clear and traceable links between packaging levels, pharmaceutical companies can better secure their products against counterfeiting, tampering, and theft. Aggregation helps verify that each product within a carton or case is accounted for, reducing the risk of fraudulent or unsafe products reaching the customer. - Simplifying Recalls and Compliance
Should a recall be necessary, aggregation simplifies the process by allowing the manufacturer to trace products efficiently and accurately through the entire supply chain. Aggregation also ensures compliance with stringent regulatory requirements, such as those set by the FDA and global track-and-trace regulations like the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA).
Steps in the Aggregation Process
- Serializing Packaging Levels
Assign unique serial numbers to each packaging level (units, cartons, cases, pallets). - Linking Parent-Child Relationships
Create the hierarchical link between the serialized units and their corresponding cartons, cases, and pallets. - Recording and Storing Aggregation Data
Store aggregation data securely in a database to enable real-time tracking, monitoring, and verification throughout the supply chain. - Integration with Warehouse and Distribution Systems
Ensure that the aggregation data is integrated with warehouse management systems (WMS) and logistics systems to maintain product visibility at all stages of distribution.
Pharmaceutical aggregation is crucial for enhancing traceability, improving safety, and ensuring regulatory compliance. By linking serialized packaging into parent-child relationships, companies can safeguard their products and maintain a secure, traceable supply chain.
Contact us today to talk to an expert at cGMP Consulting on this topic or any other compliance topic.






