
The Complete Guide to Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP)
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced industries, where safety and quality are paramount, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards is not just a necessity—it’s a competitive advantage. A single oversight can lead to recalls, fines, or even harm to consumers, making it essential for businesses to stay ahead.
Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) build on the foundation of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), adapting to modern advancements with a focus on real-time compliance, continuous improvement, and the integration of cutting-edge technologies. These practices, enforced by agencies like the FDA, set rigorous standards to ensure product safety, efficacy, and quality across industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, cosmetics, and food.
This guide explains the differences between GMP and cGMP, highlights the importance of staying “current,” and provides actionable strategies to help you implement these practices effectively. Whether you’re starting fresh or enhancing existing systems, this resource equips you to navigate the complexities of cGMP and achieve compliance with confidence.
What Sets cGMP Apart from GMP?
While GMP provides the foundation for manufacturing practices, cGMP takes it further by embracing innovation and ongoing improvements to maintain compliance with ever-changing industry demands.
Key Differences Between GMP and cGMP
- The “Current” Factor:
cGMP standards are dynamic, requiring businesses to stay updated on evolving methods, tools, and regulations. This ensures production processes remain efficient and compliant with today’s requirements. - Proactive Quality Assurance:
Unlike GMP’s foundational approach, cGMP emphasizes continuous monitoring and preventative measures to address risks—such as contamination or deviations—before they impact product quality. - Modern Updates:
- Automated systems streamline production and reduce human error.
- Electronic batch records (EBRs) enhance traceability and data accuracy.
- Real-time analytics provide immediate quality control insights.
By adopting cGMP, businesses can achieve greater operational efficiency, maintain regulatory compliance, and consistently deliver high-quality products.
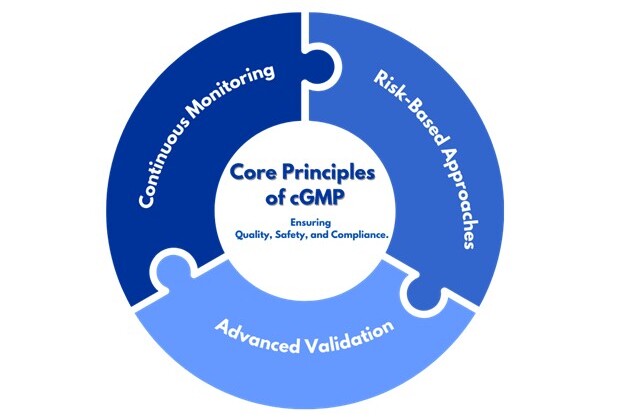
Core Principles of cGMP
cGMP is more than compliance—it’s a comprehensive approach to fostering a culture of quality, safety, and innovation.
Guiding Principles
- Risk-Based Approaches:
Proactively identify and mitigate risks at every stage of production. Address potential issues like contamination or process deviations before they affect product quality. - Continuous Monitoring:
Implement data-driven systems to track production in real time. Early detection and correction of issues ensure consistent safety and quality standards. - Advanced Validation:
Validate all processes, equipment, and systems regularly to maintain reliable outcomes. This includes verifying manufacturing methods, testing procedures, and cleaning protocols.
By adhering to these principles, businesses can:
- Comply with FDA standards and global regulations.
- Reduce inefficiencies and production waste.
- Build consumer trust by ensuring reliable product quality.
While these principles lay the foundation for a strong cGMP framework, achieving full compliance requires specific tools, strategies, and systems tailored to meet regulatory expectations. This is where key cGMP requirements come into play, guiding businesses on the practical steps needed to align their operations with modern standards.
Key cGMP Requirements: Beyond the Basics
Achieving cGMP compliance demands more than adhering to traditional GMP practices—it requires adopting modern tools and strategies to meet evolving regulatory expectations.
Essential Requirements
- Quality Management Systems (QMS):
A robust QMS provides the structure for managing compliance, audits, and continual improvement. It ensures alignment with internal and regulatory quality standards. - Electronic Record-Keeping:
Digital systems improve traceability and accuracy while streamlining compliance. For example, electronic batch records enable real-time data capture and easy audit readiness. - Supplier Qualification:
Sourcing materials from approved suppliers is critical. This involves vetting suppliers, conducting audits, and maintaining performance reviews to ensure quality and safety standards are met. - Real-Time Data Monitoring:
Continuously track critical production metrics to identify and resolve issues swiftly. This approach minimizes waste and ensures consistent product quality.
The Value of Compliance
By meeting these requirements, businesses can:
- Align with FDA and global regulatory standards.
- Minimize risks of recalls, contamination, and defects.
- Optimize operations for cost-effectiveness and reliability.
- Strengthen their reputation as a trusted, quality-driven organization.
The Role of cGMP in Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) is not just a best practice—it’s a regulatory requirement enforced by agencies like the FDA to safeguard product quality and consumer safety. Compliance ensures that manufacturing processes meet stringent standards, minimizing risks and building trust with regulators and consumers alike.
Why Compliance Matters
- FDA Expectations:
The FDA requires manufacturers to follow cGMP guidelines to ensure products are safe, effective, and consistently meet quality standards. These guidelines span across industries, adapting to specific regulatory needs while maintaining a shared focus on consumer protection. - Industry-Specific Variations:
Different industries face unique compliance challenges under cGMP:- Cosmetics: Emphasis on accurate labeling, contamination prevention, and ingredient traceability.
- Pharmaceuticals: Rigorous validation, stability testing, and controlled manufacturing environments.
- Food: Strict sanitation protocols and allergen control to prevent contamination.
- Risks of Non-Compliance:
Failure to meet cGMP standards can result in:- FDA-issued warning letters or Form 483 observations.
- Costly product recalls or manufacturing shutdowns.
- Legal penalties, reputational damage, and loss of consumer trust.
Proactive Compliance is Essential
By implementing cGMP processes, businesses not only avoid regulatory pitfalls but also enhance operational efficiency, protect their brand reputation, and position themselves for success in highly regulated markets.
Benefits of Adopting cGMP
Implementing Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) offers businesses far-reaching advantages that extend beyond regulatory compliance. By embracing cGMP, organizations can improve their operations, build consumer trust, and gain a competitive edge in their industry.
Key Benefits of cGMP
- Operational Efficiency:
Modernized processes, such as automated systems and real-time monitoring, help reduce errors, minimize downtime, and decrease waste. Streamlining workflows improves overall productivity and lowers operational costs. - Enhanced Product Consistency:
Adherence to cGMP ensures that every product batch meets stringent quality standards. This level of consistency is crucial for industries like pharmaceuticals, where even minor variations can impact safety and efficacy. - Market Readiness:
Demonstrating compliance with cGMP standards paves the way for entering global markets. Regulatory approvals often hinge on cGMP adherence, making it a critical factor for companies seeking international expansion. - Consumer Trust:
Compliance with cGMP reassures consumers that products are safe, effective, and of high quality. This commitment to excellence strengthens brand reputation and fosters long-term loyalty.
The Bigger Picture
By adopting cGMP, businesses not only meet regulatory expectations but also position themselves as leaders in quality and innovation. These practices contribute to sustainable growth, reduced risks, and increased profitability over time
Implementing cGMP in Your Organization
Transitioning from Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) is a significant step that requires strategic planning and resource allocation. A successful implementation not only ensures compliance but also sets the foundation for operational excellence and long-term growth.
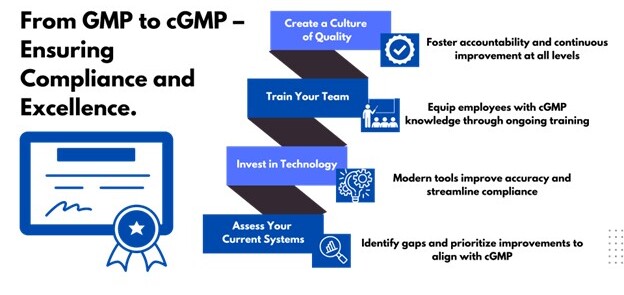
Steps to Transition to cGMP
- Assess Your Current Systems:
Begin with a comprehensive gap assessment to identify areas where existing practices fall short of cGMP standards. This analysis will help prioritize improvements and create a roadmap for compliance. - Invest in Technology:
Modern tools are essential for maintaining cGMP compliance. Consider adopting:- Automated quality management systems to streamline processes.
- Electronic records and batch systems for improved traceability and accuracy.
- Predictive analytics to anticipate risks and enhance decision-making.
- Train Your Team:
Ensure employees at all levels understand cGMP principles and their specific roles in maintaining compliance. Comprehensive, ongoing training fosters accountability and equips your team to handle evolving regulatory demands. - Create a Culture of Quality:
Cultivate an organizational mindset that prioritizes quality at every stage. Encourage proactive problem-solving, open communication, and a commitment to continuous improvement across departments. Leadership support is key to embedding this culture within the company.
Why a Strategic Approach Matters
Implementing cGMP can seem daunting, but a step-by-step approach ensures a smoother transition. Companies that invest in preparation, training, and technology not only meet compliance requirements but also reap the rewards of improved efficiency, reduced risks, and stronger market positioning.
Common Challenges in cGMP Compliance
Implementing Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) offers significant benefits, but the process is not without its hurdles. Understanding these challenges can help businesses proactively address them and ensure a smoother transition to compliance.
Top Challenges in cGMP Compliance
- Resistance to Change:
Employees may be reluctant to adopt new systems or workflows, particularly if they are unfamiliar with advanced technologies or fear additional workload. - Cost of Modernization:
Upgrading facilities, equipment, and software to meet cGMP standards often requires significant financial investment. Smaller organizations may face difficulties allocating resources for these improvements. - Global Supply Chains:
Ensuring consistent compliance across international suppliers adds complexity. Variations in local regulations, supplier capabilities, and communication channels can create gaps in quality management.
Strategies to Overcome cGMP Challenges
- Clear Communication:
Explain the benefits of cGMP implementation to employees at all levels, highlighting how it improves efficiency, reduces risks, and secures the company’s reputation. - Phased Implementation:
Break the process into manageable steps, focusing on high-priority areas first. This approach minimizes disruption while allowing for continuous progress toward full compliance. - Leverage Expert Support:
Partner with experienced consultants who specialize in cGMP compliance. Their expertise can help identify potential pitfalls, streamline implementation, and ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
By addressing these challenges with a proactive and strategic approach, businesses can achieve cGMP compliance while minimizing disruptions and maximizing long-term benefits.
The Future of cGMP
As industries evolve, Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) will adapt to keep pace with advancements in technology, shifts in consumer expectations, and the growing demand for sustainability. These changes will shape the next generation of cGMP, driving innovation and redefining compliance standards.
Emerging Trends in cGMP
- Personalized Medicine:
The rise of personalized treatments, such as gene therapies and customized pharmaceuticals, will require cGMP processes to become even more flexible and precise to accommodate small-batch, high-complexity manufacturing. - Blockchain for Supply Chain Traceability:
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to trace raw materials and products throughout the supply chain. Its integration into cGMP compliance will enhance accountability and reduce risks of counterfeiting or contamination. - AI-Driven Quality Control:
Artificial intelligence (AI) is set to revolutionize quality management. From predictive maintenance of equipment to real-time anomaly detection, AI will enable faster, more accurate decision-making in compliance processes.
The Role of Sustainability in cGMP
As global attention shifts toward environmental responsibility, cGMP standards will increasingly incorporate sustainability metrics. Key areas of focus may include:
- Eco-Friendly Manufacturing: Implementing energy-efficient equipment and reducing waste through circular manufacturing practices.
- Green Packaging Solutions: Using recyclable and biodegradable materials that align with cGMP standards while meeting consumer demand for environmentally conscious products.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Monitoring and minimizing emissions throughout the production lifecycle to align with both regulatory goals and consumer values.
Looking Ahead
The future of cGMP will be defined by its ability to adapt and innovate. Companies that embrace these advancements will not only ensure compliance but also gain a competitive edge in delivering high-quality, sustainable, and cutting-edge products to the market.
Why cGMP Compliance is Crucial for Your Business
Adhering to Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) is more than just a regulatory obligation—it’s a strategic investment that positions your business for long-term success. Beyond meeting compliance requirements, cGMP drives operational excellence, strengthens consumer trust, and enhances your competitive edge.
The Business Case for cGMP Compliance
- Avoid Penalties and Regulatory Issues:
Non-compliance with cGMP standards can result in costly FDA-issued Form 483 observations, warning letters, or even product recalls. By implementing robust cGMP practices, businesses can proactively address potential violations and maintain regulatory readiness. Learn more about FDA Form 483 and how to respond effectively. - Gain Consumer Trust:
Today’s consumers expect high-quality, safe, and reliable products. Adherence to cGMP showcases your commitment to quality and innovation, building trust with your customers and reinforcing your brand reputation. - Strengthen Market Position:
Companies that demonstrate proactive compliance set themselves apart from competitors. Meeting cGMP standards not only ensures product quality but also facilitates access to global markets and regulatory approvals. Businesses aligned with cGMP are better equipped to adapt to new market opportunities and expand their reach.
The FDA’s Role in cGMP Compliance
The FDA plays a critical role in enforcing cGMP regulations across industries, conducting inspections, and issuing guidance to ensure public health and safety. Staying compliant minimizes risks while positioning your business as a trusted partner in regulated markets. Read more about FDA inspections and compliance requirements here.
A Strategic Advantage
cGMP compliance isn’t just about avoiding fines—it’s about creating a foundation for sustainable growth, innovation, and operational efficiency. Businesses that invest in cGMP position themselves as industry leaders, ready to meet the challenges of an evolving regulatory landscape.
Conclusion
Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) are more than regulatory guidelines—they are the cornerstone of operational excellence and consumer trust. By adopting cGMP, businesses can ensure product quality, safety, and compliance while positioning themselves as leaders in their industries.
In today’s competitive market, staying “current” is not optional—it’s essential. Embracing cGMP allows your business to meet evolving regulatory demands, reduce risks, and build a reputation for reliability and innovation.
Don’t wait to take action. Elevate your operations today by implementing cGMP compliance strategies tailored to your unique needs. Our team of experts is here to guide you every step of the way. Contact us now for a free consultation and take the first step toward building a stronger, more compliant future.
“This post was developed with input from our GMP experts and crafted by our SEO and blogging specialist, Tayler Awad, to enhance accessibility and online reach.”





