Cross-Contamination Risk Assessments
Managing the Unintended Transfer of Contaminants
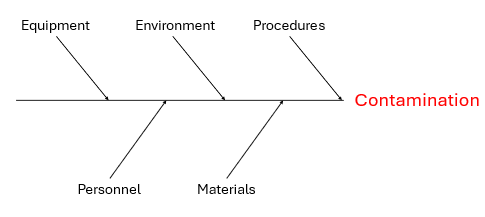
A cross-contamination risk assessment is a systematic evaluation of potential sources and pathways of contamination within a production process. The goal is to identify, evaluate, prioritize, and mitigate risks associated with the unintended transfer of contaminants as shown in the Fishbone diagram below.
Key Considerations in Cross-Contamination Risk Assessments
The process of conducting a cross-contamination risk assessment typically involves several critical steps:
- Scope Definition: Define the scope of the risk assessment, including the products, processes, and areas to be evaluated. Determine the specific contaminants of concern based on the nature of the products and manufacturing processes involved.
- Identification of Potential Contaminants: Identify potential sources of contamination within the production process, including raw materials, equipment, personnel, and environmental factors. Consider factors such as allergens, pathogens, chemicals, or other substances that may pose a risk to product safety or quality.
- Assessment of Likelihood and Severity: Assess the likelihood of cross contamination occurring and the severity of its potential impact on product quality or safety. Consider factors such as the frequency of contact between sources of contamination, potency of the contaminant, and potential consequences for consumers.
- Evaluation of Control Measures: Evaluate existing control measures to prevent or mitigate cross contamination risks, including cleaning and sanitation procedures, equipment design features, personnel training, and process/material segregation.
- Identification of Critical Control Points (CCPs): Identify CCPs within the production process where control measures can be implemented to prevent or minimize cross contamination. Focus on areas most susceptible to contamination or with the greatest impact on product quality/safety.
- Risk Ranking and Prioritization: Rank and prioritize cross contamination risks based on the likelihood, severity, and effectiveness of existing control measures. Address high-risk areas first to ensure significant risks are mitigated adequately.
- Development of Risk Mitigation Strategies: Develop and implement risk mitigation strategies to reduce the likelihood and severity of cross contamination events. This may involve implementing additional control measures, modifying process or equipment design, or enhancing personnel training and hygiene practices.
- Monitoring and Verification: Establish procedures for monitoring and verifying the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies over time. Regularly review and update the cross-contamination risk assessment to ensure that control measures remain effective amidst changes in production processes or environmental conditions change.
- Documentation and Review: Document the cross-contamination RA process and its outcomes, including identified risks, control measures, and risk mitigation strategies. Regularly review and update the documentation to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and continuous improvement of risk management practices.
By conducting a thorough cross-contamination risk assessment, companies can identify hazards and implement appropriate control measures to prevent or minimize contamination risks. This ensures the safety, efficacy, and quality of their products, aligning with regulatory standards and consumer expectations.
Conclusion
Conducting a comprehensive cross-contamination risk assessment is essential for maintaining product safety, quality, and regulatory compliance. By carefully evaluating potential contamination sources, assessing control measures, and implementing risk mitigation strategies, companies can proactively prevent contamination risks within their production processes.
For a deeper dive into this topic, take a look at our related article.
Contact us to learn more about how cross-contamination risk assessments can enhance your manufacturing practices and align with industry standards for product safety. cGMP Consulting can help with all your compliance needs and questions.