Get FDA Ready: How Manufacturers Can Master Internal Audits in 2025
Internal audits play a critical role in helping manufacturers stay compliant, maintain product quality, and improve operational efficiency. For FDA-regulated companies, they ensure processes meet regulatory standards while identifying and mitigating potential risks. Follow these practical steps to conduct effective internal audits and achieve FDA compliance.
Why Internal Audits Are Critical for FDA Compliance
Internal audits are vital for achieving and maintaining FDA compliance. They help manufacturers ensure processes align with regulatory standards while identifying areas for improvement. Key benefits include:
- Ensuring regulatory compliance by aligning operations with GMP, ISO standards, and FDA guidelines.
- Spotting non-conformities to address gaps and improve operational standards.
- Mitigating risks by resolving compliance issues proactively.
- Boosting efficiency through optimized workflows and reduced waste.
Action Tip: Clearly define your audit objectives to align with company goals and regulatory requirements.
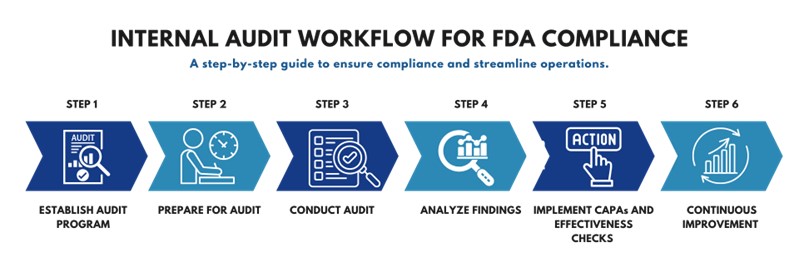
Step 1: Establish Your Internal Audit Program
A well-defined audit program is crucial to meeting FDA compliance requirements in 2025. Key elements of an effective program include:
- Audit scope and frequency: Determine which areas to audit and how often based on risk assessments.
- Audit checklist: Develop detailed checklists tailored to regulatory requirements and internal standards.
- Audit team selection: Choose trained auditors who are independent of the processes being audited.
Action Tip: Use software tools to schedule and manage audits, ensuring no critical areas are overlooked.
Step 2: Prepare for the Audit
Proper preparation ensures a smooth and effective audit process. Key preparatory steps include:
- Reviewing relevant documents: Collect SOPs, batch records, and previous audit reports.
- Notifying departments: Inform relevant teams about the audit schedule and scope.
- Setting up interviews: Plan to interview employees to understand processes and identify potential gaps.
Action Tip: Create a pre-audit checklist to ensure all necessary documents and personnel are ready.
Step 3: Conduct the Audit
During the audit, focus on these critical areas to ensure thoroughness:
- Document review: Verify that procedures and records are current and meet regulatory and company standards.
- Process observation: Walk through production areas to observe operations and identify potential issues.
- Employee interviews: Ask questions to assess their understanding of procedures and compliance.
- Identify non-conformities: Document any deviations or areas needing improvement.
Action Tip: Use mobile devices or tablets to take real-time notes and photos for accurate documentation.
Step 4: Analyze and Report Audit Findings
Analyzing and reporting findings accurately is essential for driving compliance and operational improvements. Focus on:
- Categorizing findings: Classify non-conformities based on severity (critical, major, minor).
- Root cause analysis: Determine the underlying causes of non-conformities.
- Audit report: Prepare a detailed report with findings, corrective actions, and deadlines for resolution.
Action Tip: Use templates for consistent reporting and ensure reports are reviewed by senior management.
Step 5: Implement Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
Addressing audit findings quickly ensures sustained compliance and process improvements. Key actions include:
- Developing CAPA plans: Outline specific actions to correct and prevent identified issues.
- Assigning responsibilities: Designate team members to implement CAPAs and track progress.
- Conducting Effectiveness checks: Regularly review CAPAs to ensure they resolve the issues effectively and do not lead to recurring events.
Action Tip: Leverage CAPA tracking software to streamline implementation and reporting.
Step 6: Continuous Improvement and Follow-Up
Sustaining compliance requires an ongoing cycle of improvements. Key follow-up actions include:
- Re-auditing: Schedule follow-up audits to verify the effectiveness of corrective actions.
- Updating procedures: Revise SOPs and training materials based on audit findings.
- Sharing lessons learned: Communicate audit outcomes and improvements across departments to prevent future issues.
Action Tip: Create a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging feedback and innovation from all employees.
Final Thoughts
In 2025, internal audits are not just a regulatory requirement but a powerful tool for driving operational excellence. By implementing a well-structured audit program, manufacturers can stay ahead of regulatory changes, enhance product quality, and build trust with stakeholders. Remember, the key to successful audits lies in preparation, thoroughness, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
If you’re looking for expert guidance on internal auditing, our team at cGMP Consulting Inc. can help you develop and implement a robust audit program tailored to your needs. Contact us today for a free consultation!
“This post was developed with input from our GMP experts and crafted by our SEO and blogging specialist, Tayler Awad, to enhance accessibility and online reach.”